Research Interests
Research Interests
White matter-activated microgliosis and cognitive impairment
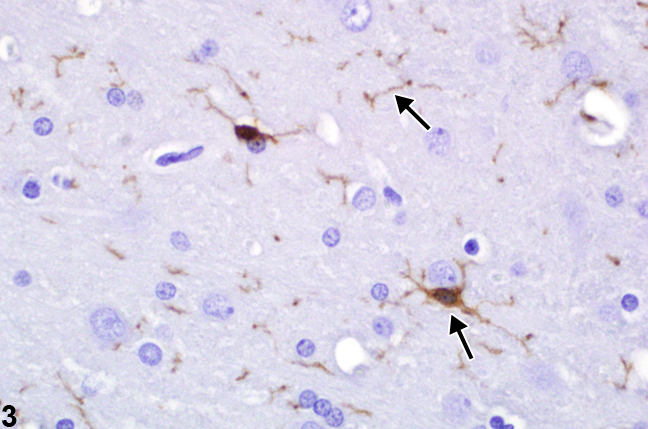
- A.D. Roseborough, V. Hachinski and S.N. Whitehead. White matter degeneration – a treatable target? JAMA Neurol. 2020 Apr 27.
- A. Levit, S. Cheng, O. Hough, Y. Agca, C. Agca, V. Hachinski and S.N. Whitehead. Hypertension and pathogenic hAPP independently induce white matter astrocytosis and cognitive impairment in the rat. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Apr 15;12:82.
- N. Ivanova, Q. Liu, C. Agca, Y. Agca, E.G. Noble, S.N. Whitehead and D.F. Cechetto. White matter inflammation and cognitive function in a co-morbid metabolic syndrome and prodromal Alzheimer’s disease rat model. J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jan 21;17(1):29.
- A. Levit, A.M Regis, A. Gibson, O.H. Hough, S. Maheshwari, Y. Acga, C. Agca, V. Hachinski, B.L Allman and S.N. Whitehead. Impaired behavioural flexibility related to white matter microgliosis in the TgAPP21 rat. Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Feb 15. pii: S0889-1591(18)30617-2.
- N. Weishaupt*, Q. Liu*, S. Shin, R. Singh, Y. Agca, C. Agca, V. Hachinski and S.N. Whitehead. APP21 transgenic rats develop age-dependent cognitive impairment and microglia within white matter tracts. J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 28;15(1):241. * Both authors contributed equally.
- Levit, A.M Regis, A. Gibson, O.H. Hough, S. Maheshwari, Y. Acga, C. Agca, V. Hachinski, B.L Allman and S.N. Whitehead. Impaired behavioural flexibility related to white matter microgliosis in the TgAPP21 rat. Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Feb 15. pii: S0889-1591(18)30617-2.
Understanding how inflammation is propogated
Chronic peripheral inflammation drives brain inflammation and vice versa. Our lab is focused on driving mechanisms related to this bi-directional communication. For example, we’ve shown that cardiac fibrosis occurs following stroke. Current projects are aimed at understanding the molecular mechanisms expalining the links between peripheral and central inflammation with a focus on autonomic dysregulation and extracellular vesicle dependent communication.
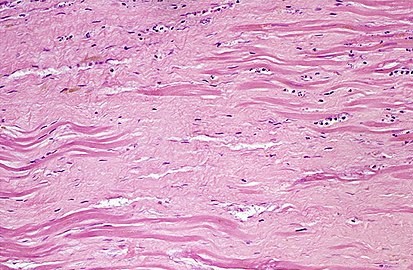
- V.M. Jaremek, S.N. Whitehead and L.A. Sposato. Lateralization of the control of cardiovascular autonomic function and left atrial injury after selective right and left insular stroke. Int J Cardiol. 2019 Nov 1;294:15.
- V. Hachinski, K. Einhaupl, D. Ganten, S. Alladi, C. Brayne, B.C.M. Stephan, Z. Khachaturian, M. Sweeney, B. Zlokovic, Y. Iturria-Medina, C. Iadecola, N. Nishimura, C.B. Schaffer, S.N. Whitehead, S.E. Black, L. Ostergaard, J. Wardlaw, S. Greenberg, L. Friberg, B. Norrving, B. Rowe, Y. Joanette, W. Hacke, L. Kuller, M. Dichgans and M. Endres. Preventing dementia by preventing stroke: The Berlin Manifesto. Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Jul;15(7):961-984.
- B. Balint*, V. Jaremek*, V. Thorburn, M. Paquet, S.N. Whitehead* and L.A. Sposato*. Left atrial endothelial dysfunction, inflammation and fibrosis induced by selective insular cortex ischemic stroke in rats. Int J Cardiol. 2019 Oct 1;292:148-155. * Both authors contributed equally.
- B. Halvorsron, S.N. Whitehead, J. McGuire, R. Wiseman, and J. Frisbee. Endothelium-dependent impairments to cerebral vascular reactivity with type-II diabetes mellitus in the Goto-Kakizaki rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019 Jul 1;317(1):R149-R159.
- L.A. Sposato, S. Fridman, S.N. Whitehead and R.D. Lopes. Linking stroke-induced heart injury and neurogenic atrial fibrillation: a hypothesis to be proven. J Electrocardiol. 2018 Feb 20.
Multimodal imaging of regulators of vulnerability in the brain
An understanding of molecules that render the brain vulnerable to disease, in particular within the white matter depend on complementary and sophisticated imaging approaches. This imaging modalities include MRI, PET and mass spectrometry imaging. Current research is aimed at combining these imaging modalities in cells, pre-clinical animal models and human brain tissue.
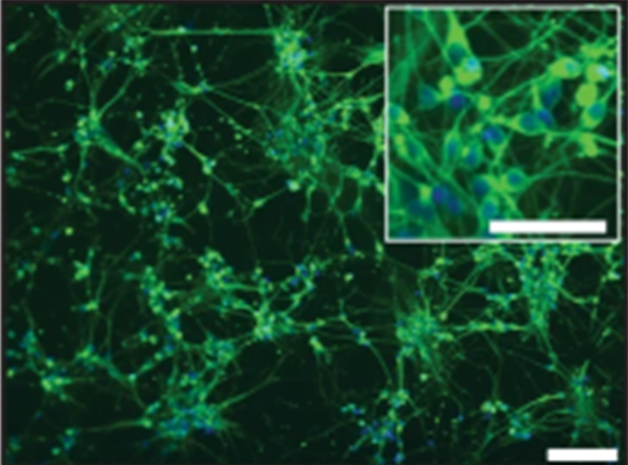
- Y. Dong, C. D’Mello, W. Pinsky, B. Lozinski, D. Kaushik, S. Ghorbanigazar, D. Moezzi, D. Brown, F. Melo, T. Vo, S. Zandee, A. Prat, S.N. Whitehead and V.W. Yong. Oxidized phosphatidylcholines promote neurodegeneration and are neutralized by microglia. Accepted, Nature Neuroscience (2021).
- W.J. Pinsky, A. Harris, A.D. Roseborough, W. Wang, K. Jurcic, A.R. Khan, K.K.C. Yeung, S.H. Pasternak, and S.N. Whitehead. Regional lipid expression abnormalities identified using MALDI-IMS correspond to MRI-defined white matter hyperintensities within post-mortem human brain tissue. Accepted, Analytical Chemistry (2021).
- N.U. Al-Khishman, Q. Qi, A.D. Roseborough, A. Levit, M.S. Fox, S.N. Whitehead* and J.D. Thiessen*. TPSO PET detects acute neuroinflammation but not diffuse chronically activated MHCII microglia in the rat. Accepted, European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Research 2020 Sep 29;10(1):113. * Both authors contributed equally.
- S.C. Caughlin, J. Hepburn, Q. Liu, L. Wang, K.K.C Yeung, D.F. Cechetto and S.N. Whitehead. Chloroquine restores ganglioside homeostasis and improves pathological and behavioural outcomes post-stroke in the rat. Mol Neurobiol. 2019 May;56(5):3552-3562.
- S.C. Caughlin, S. Maheshwari, Y. Agca, C. Agca, K.K.C. Yeung, D.F. Cechetto and S.N. Whitehead. Membrane-lipid homeostasis in a prodromal rat model of AD: Characteristic shifts in ganglioside abundance during aging detected using MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2018 Mar 13;1862(6):1327-1338. **Featured in BBA Collection on Cellular Aging and Senescence.
- J.R. Plemel, N.J. Michaels, N. Weishaupt, A.V. Caprariello, M.B. Keough, J.A Rogers, A. Yuseloglu, J. Lim, V.V. Patel, K.S. Rawji, S.K. Jensen, W. Teo, B. Heyne, S.N. Whitehead, P.K. Stys and V.W. Yong. Mechanisms of lysophosphatidylcholine-induced demyelination: a primary lipid disrupting myelinopathy. Glia. 2018 Feb;66(2):327-347.